
Image result for oxidative and substrate level phosphorylation
What You'll Learn? 1 Substrate Level Phosphorylation vs Oxidative Phosphorylation 1.1 What is Substrate Level Phosphorylation? 1.1.1 Examples of Substrate Level Phosphorylation 1.1.2 Uses of Substrate Level Phosphorylation 1.2 What is Oxidative Phosphorylation? 1.2.1 Examples of Oxidative Phosphorylation 1.2.2 Uses of Oxidative Phosphorylation

Substrate Level Phosphorylation vs Oxidative Phosphorylation neetpg
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: the energy-requiring phase, above the dotted line in the image below, and the energy-releasing phase, below the dotted line. Energy-requiring phase. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are.
Compare and contrast substratelevel phosphorylation and oxidativ
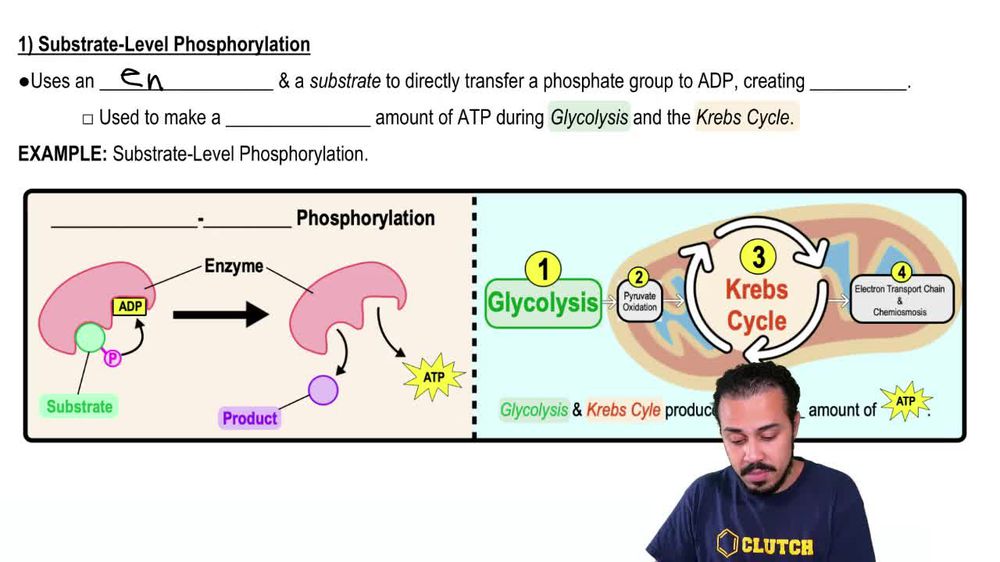
Thus, substrate level phosphorylation is used during fermentative growth, whereas both substrate level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation are used during respiratory growth. Substrate level phosphorylation. The direct formation of ATP from ADP is linked to the hydrolysis of certain phosphorylated intermediates of the catabolic pathways.

substrate level vs oxidative phosphorylation
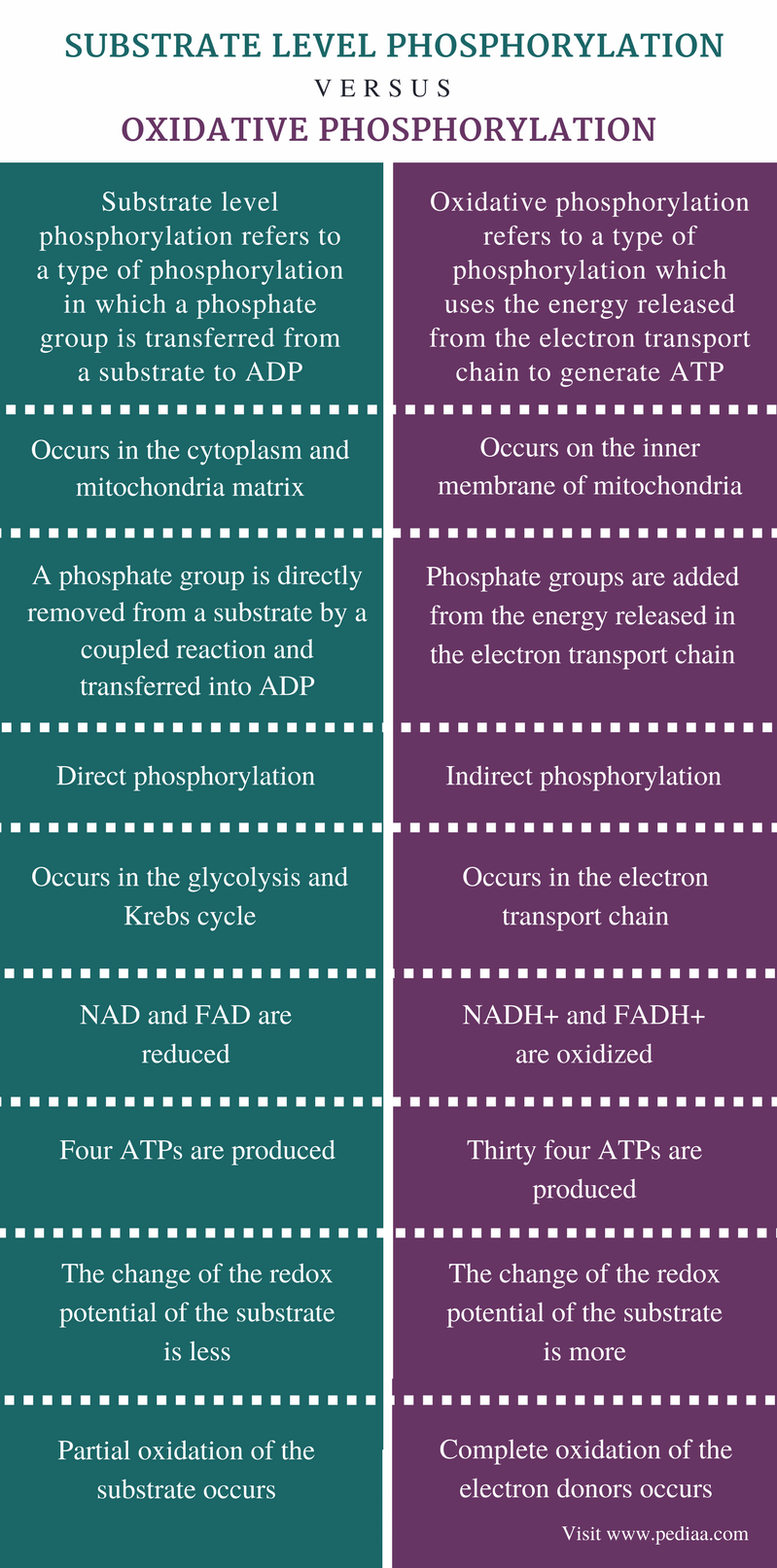
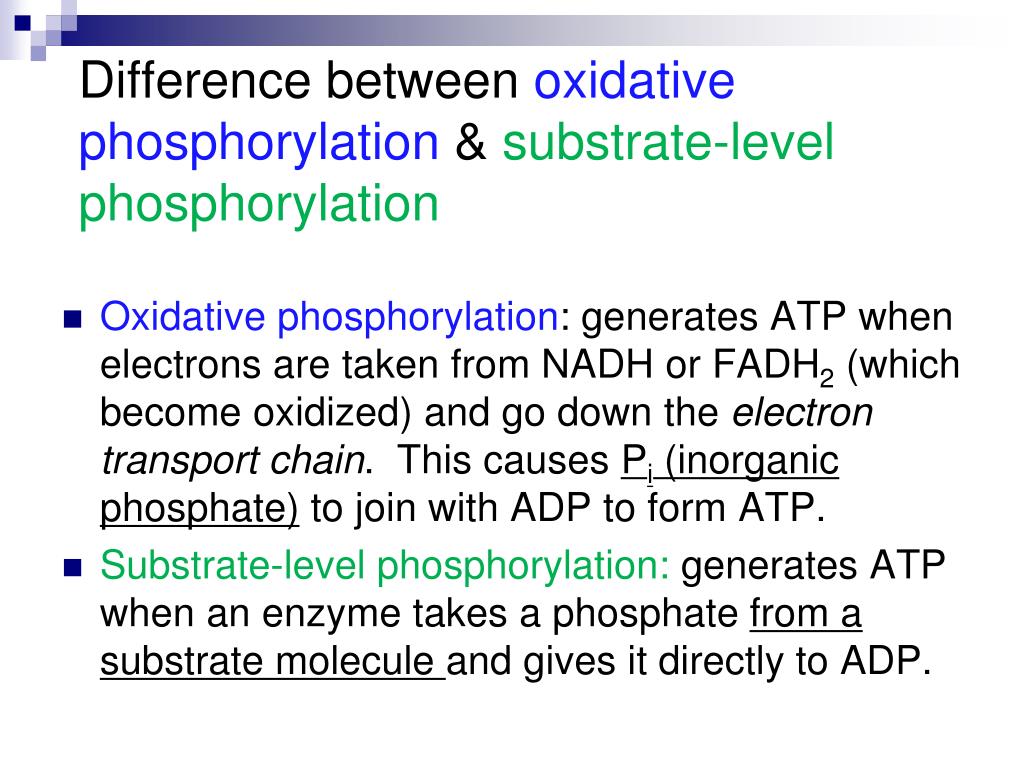
The main difference between substrate level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation is that substrate level phosphorylation is a direct phosphorylation of ADP with a phosphate group by using the energy obtained from a coupled reaction whereas oxidative phosphorylation is the production of ATP from the oxidized NADH and FADH2.
When Substrate Level Phosphorylation Occurs It Means That
Overall, the theoretical maximum yield of ATP made during the complete aerobic respiration of glucose is 38 molecules, with four being made by substrate-level phosphorylation and 34 being made by oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 8.16). In reality, the total ATP yield is usually less, ranging from one to 34 ATP molecules, depending on whether.
oxidative vs substrate level phosphorylation
Over 27,000 video lessons and other resources, you're guaranteed to find what you need. Learn faster. Stay motivated. Study smarter.
PPT Cellular Respiration Electron Transport Chain Ch. 9 PowerPoint
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a process that occurs during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle. It takes place in order to form high-energy ATPs for cellular and biological processes in the body.

What is the difference between substrate level phosphorylation and
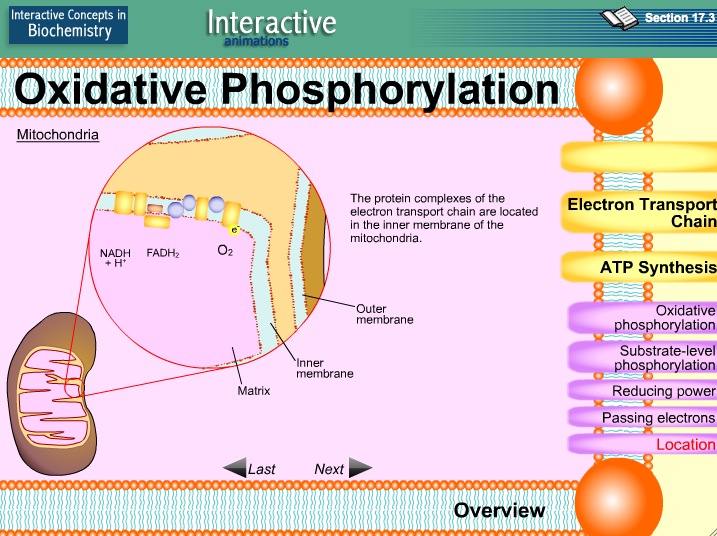
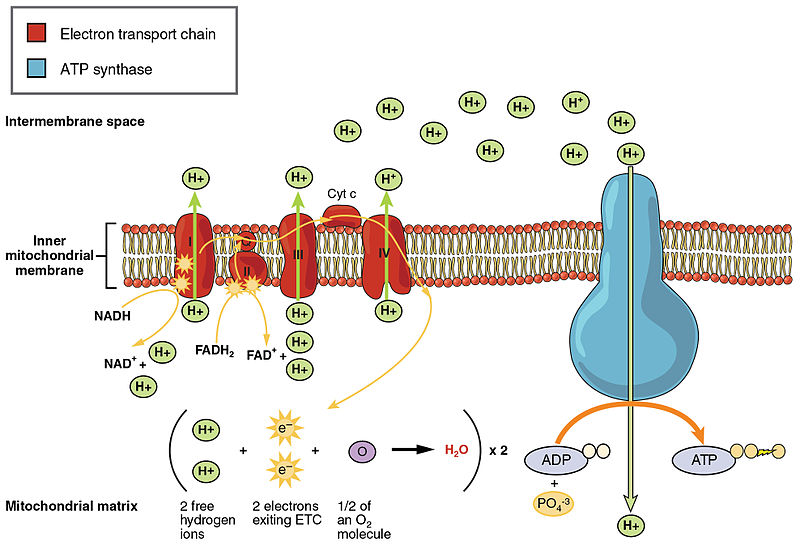
Oxidative phosphorylation is a cellular process that harnesses the reduction of oxygen to generate high-energy phosphate bonds in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is a series of oxidation-reduction reactions that involve the transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen across several protein, metal, and lipid complexes in the mitochondria known as the electron transport chain.

Image result for oxidative and substrate level phosphorylation Redox
Substrate-level phosphorylation means that a phosphate is transferred to ADP from a high-energy phosphorylated organic compound. We will see in the section on metabolic pathways that a couple of the enzymes in glycolysis make ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation, as well as an enzyme in the citric acid cycle. However, only a small amount.
.PNG)
SubstrateLevel Phosphorylation
Figure 17.5.1 17.5. 1: ATP Production during Aerobic Respiration by Oxidative Phosphorylation involving an Electron Transport System and Chemiosmosis. NADH and FADH 2 carry protons (H +) and electrons (e -) to the electron transport chain located in the membrane. The energy from the transfer of electrons along the chain transports protons.
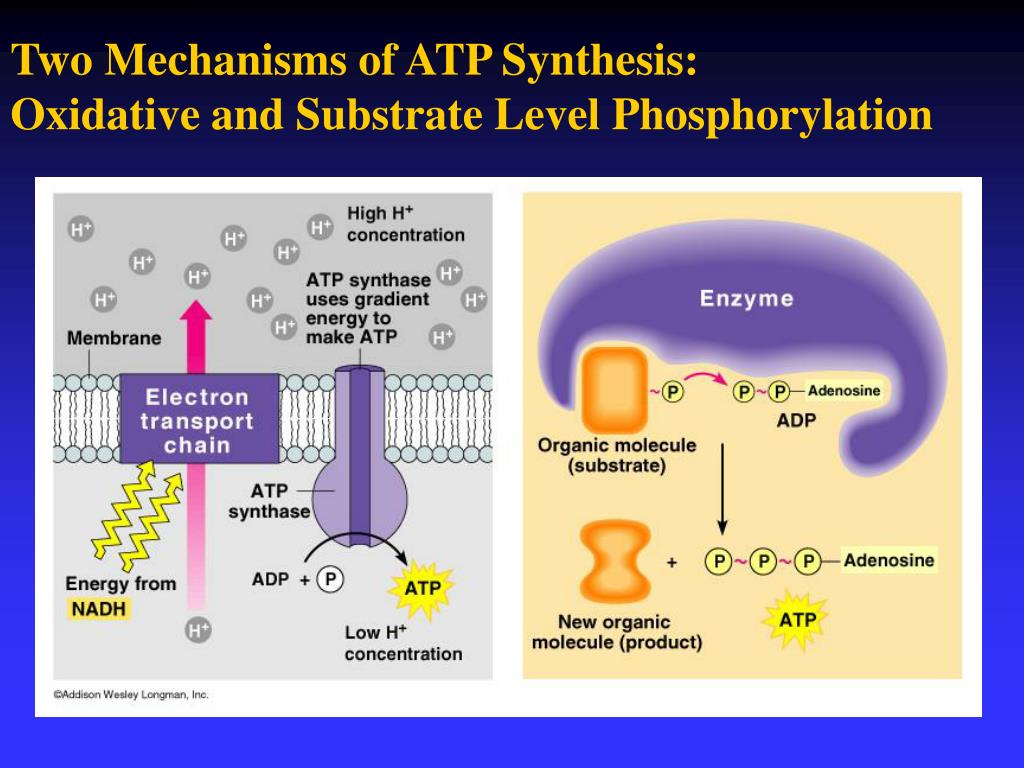
PPT Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy PowerPoint
The main difference between substrate level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation is that substrate level phosphorylation is a direct phosphorylation of ADP with a phosphate group.
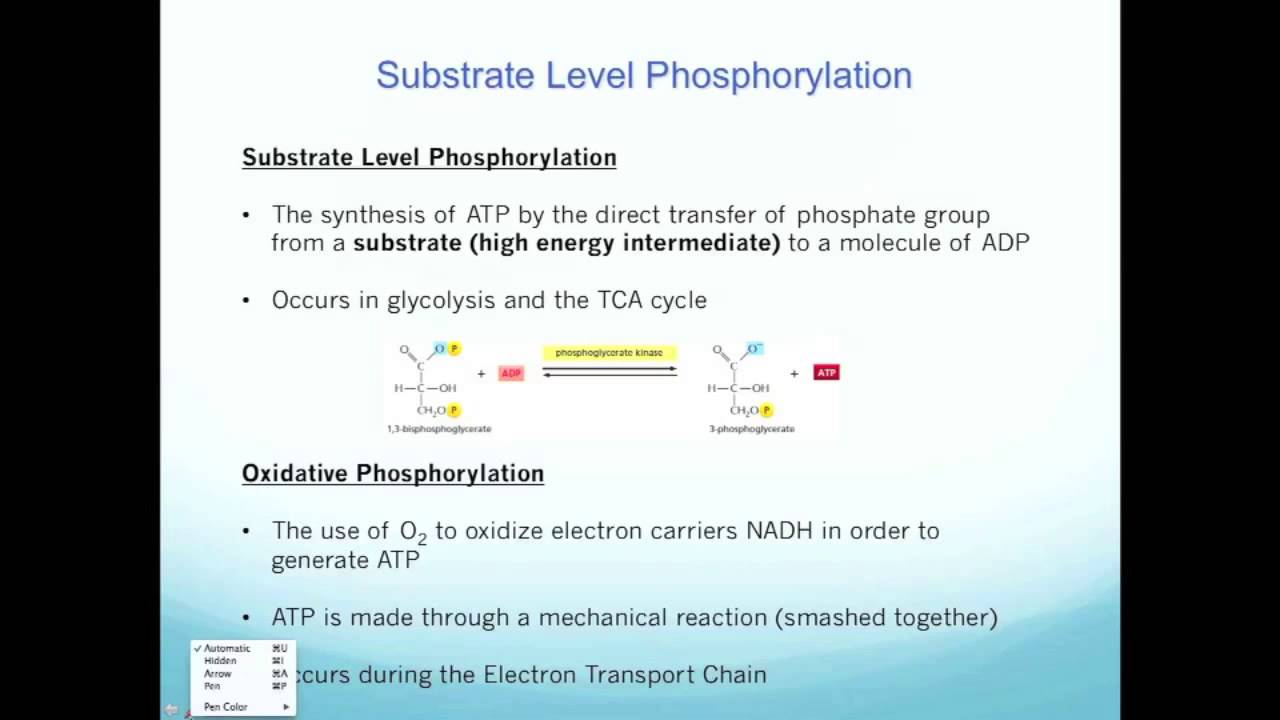
Substrate level vs. Oxidative Phosphorylation YouTube
Substrate-level vs. oxidative phosphorylation. Electron carriers. Introduction Let's imagine that you are a cell. You've just been given a big, juicy glucose molecule, and you'd like to convert some of the energy in this glucose molecule into a more usable form, one that you can use to power your metabolic reactions. How can you go about this?
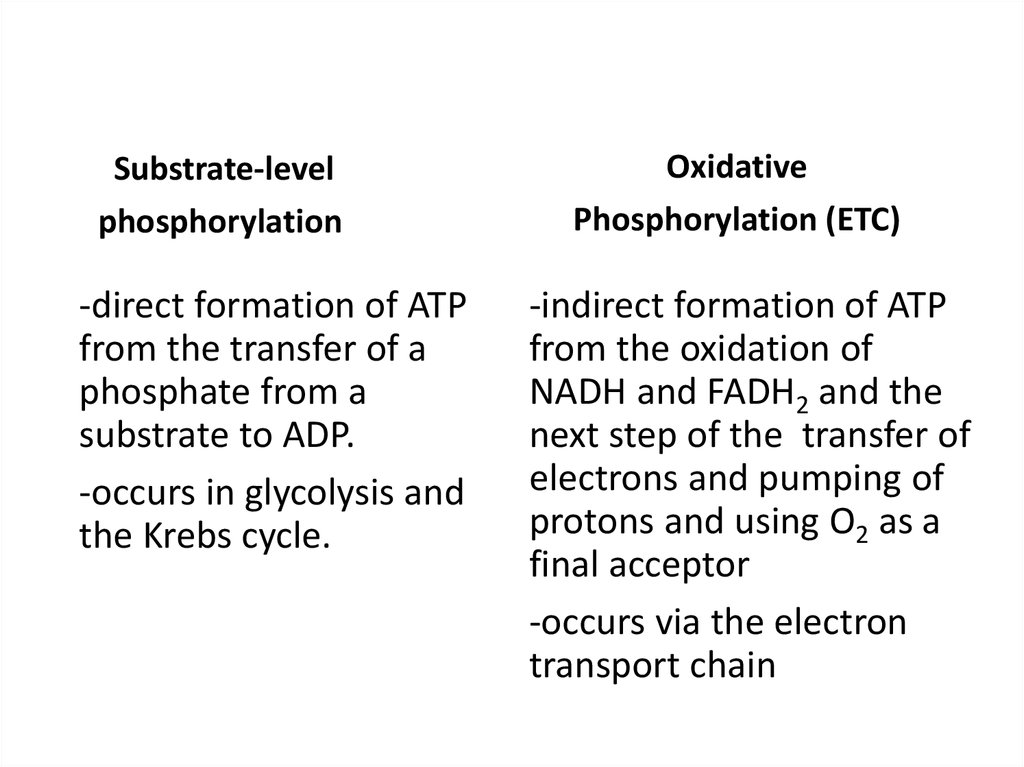
Cellular Respiration (part 3) Etc And Oxidative Phosphorylation 3EC
Figure 7.12.1 7.12. 1: Chemiosmosis: In oxidative phosphorylation, the hydrogen ion gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP. If the membrane were open to diffusion by the hydrogen ions, the ions would tend to spontaneously diffuse back across into the matrix, driven by their electrochemical gradient.
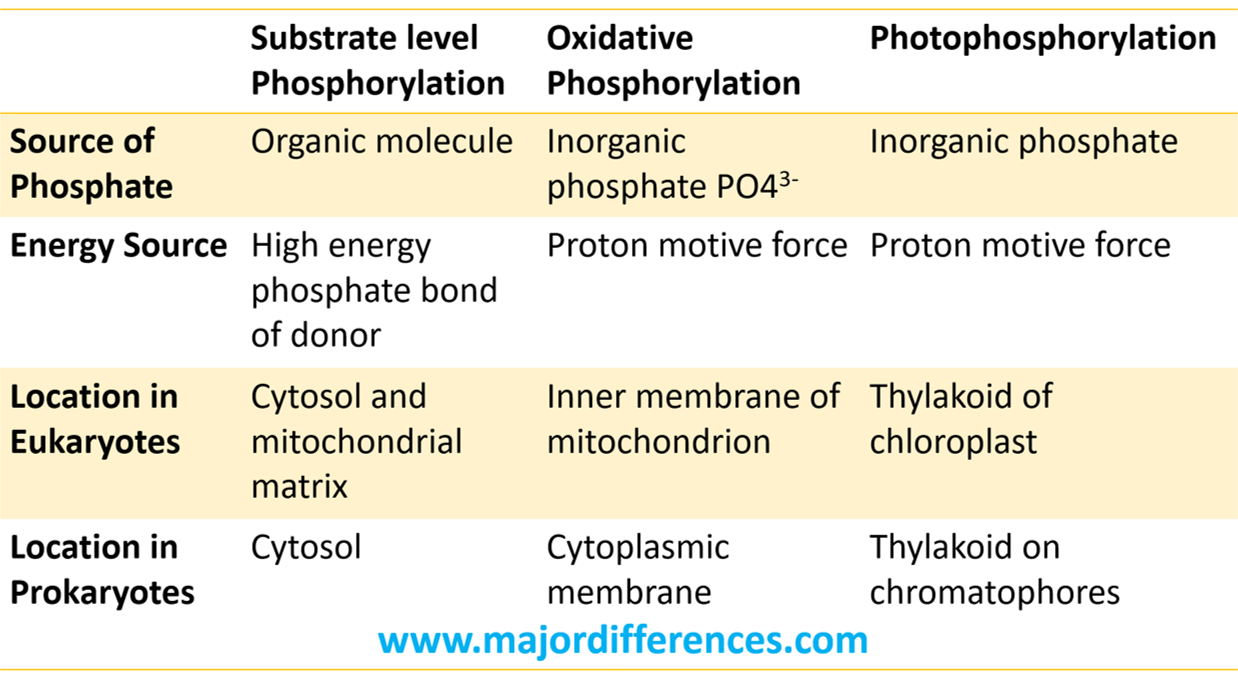
Difference between Substrate level phosphorylation, Oxidative
Most ATP is generated by oxidative phosphorylation in aerobic or anaerobic respiration while substrate-level phosphorylation provides a quicker, less efficient source of ATP, independent of external electron acceptors. This is the case in human erythrocytes, which have no mitochondria, and in oxygen-depleted muscle. Overview

Oxidative Phosphorylation Diagram
Substrate-level phosphorylation is an exergonic reaction that is responsible for the transfer of a phosphoryl group from a substrate to a nucleoside diphosphate (ADP or GDP) to form a.
Difference Between Substrate Level Phosphorylation and Oxidative
Oxidative phosphorylation is a vital cellular respiration process that generates ATP. It involves the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 and phosphorylation. The process creates a hydrogen gradient, enabling chemiosmosis and ATP synthesis. This energy conversion is essential for all life forms, from bacteria to sharks. Created by Sal Khan. Questions